Heterocyclic Chemistry
Heterocycles are crucial components of imortant molecules found across all facets of every day life.
This course of videos aims to provide a rigourous foundation of heterocyclic chemistry.
A PDF Handout to accompany these lectures is available for download: PDF.
All the videos have been complied to a YouTube playlist: YouTube.
Total running time: 4 hrs 16 mins.

01: Introduction to Heterocyclic Chemistry [06:46]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
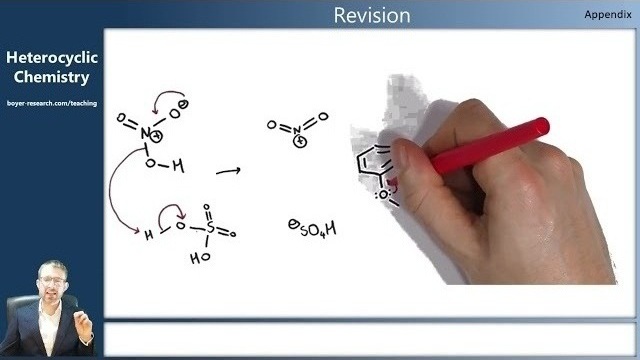
02: Revision of Key Concepts [14:09]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
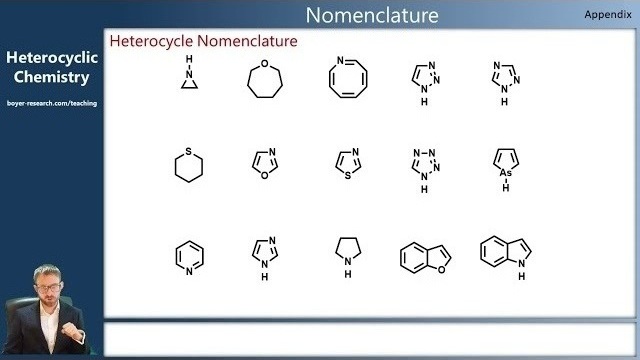
03: Heterocycle Nomenclature [18:47]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
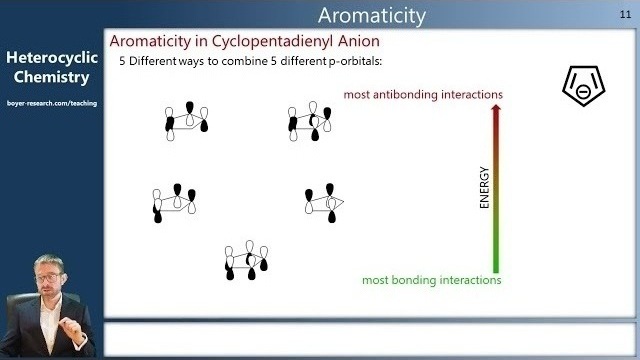
04: Aromaticity [07:48]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
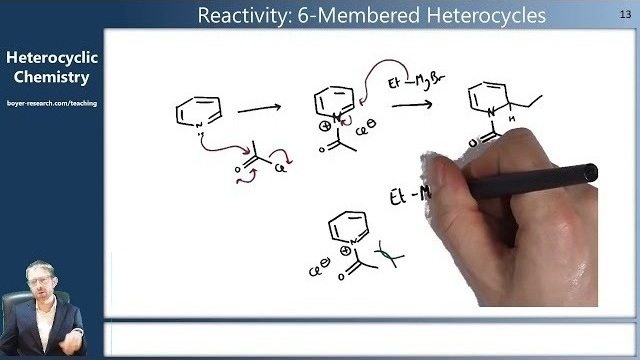
05: Reactivity of 6-Membered Aromatic Heterocycles - Part 1 [29:07]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
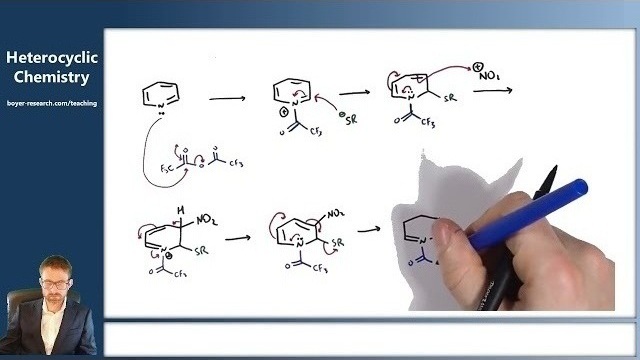
06: Reactivity of 6-Membered Aromatic Heterocycles - Part 2 [16:57]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube

07: Reactivity of 6-Membered Aromatic Heterocycles - Part 3 [12:40]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
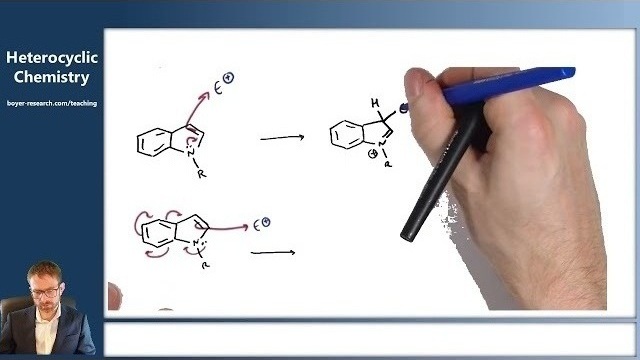
08: Reactivity of 5-Membered Aromatic Heterocycles [19:01]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
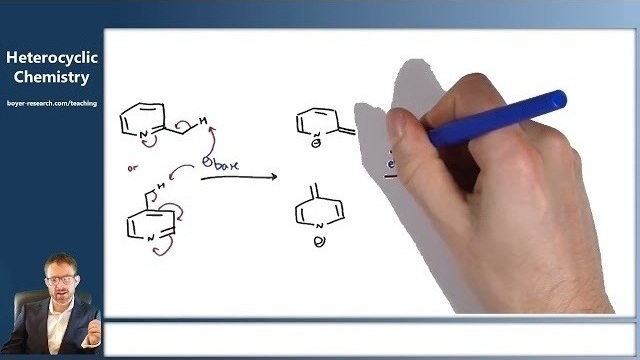
09: General Reactivity of Heterocycles [27:06]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
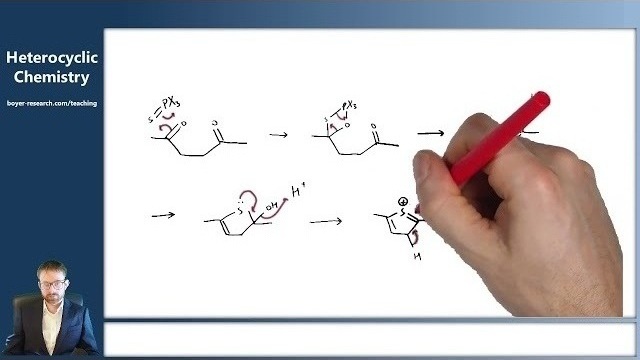
10: Strategy for Heterocycle Synthesis:Cyclisation and Dehydration[29:39]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube

11: Synthesis of Furans and Pyrroles [14:41]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
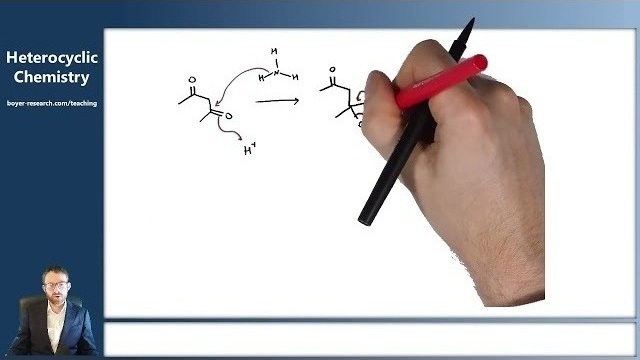
12: Synthesis of Pyridines [14:49]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
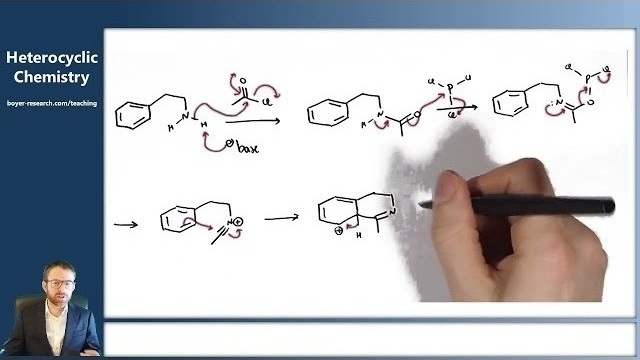
13: Synthesis of Isoquinolines and Quinolines [22:39]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
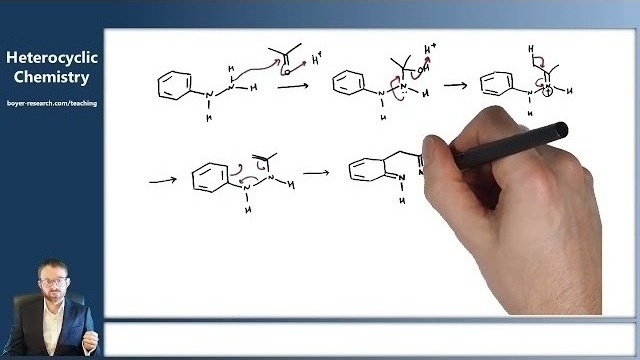
14: Synthesis of Indoles [10:25]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
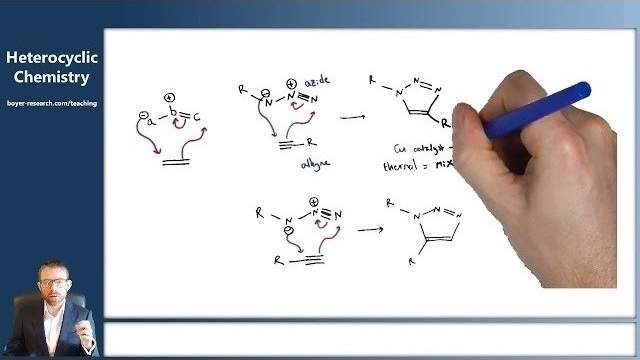
15: Heterocycle Synthesis by 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition [11:42]
Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
Course Outline and Aims
- Identify and name the most commonly found and most important heterocycles;
- Work out when a heterocycle is aromatic and appreciate the different ways in which a heteroatom can contribute to aromaticity;
- Explain the reactivity and behaviour of different classes of heterocycles and substituted heterocycles;
- Recognise how the structure and reactivity of heterocycles containing two or more heteroatoms correlates with heterocycles possessing a single heteroatom;
- Devise or explain the synthesis of key heterocycles based upon basic functional group chemistry and classical heterocyclic syntheses;
- Devise or explain the synthesis of heterocycles containing two or more heteroatoms and recognise the relationship to the syntheses of those containing a single heteroatom; and
- Appreciate the pivotal importance of heterocycles in important molecules.